Over the past decade, emerging countries in the Middle East — such as Iraq, Ethiopia, and Pakistan — have shown complex economic dynamics characterized by transition processes, structural reforms, and efforts to stabilize their markets. Among these, Iraq stands out for the significant recovery of its currency, the Iraqi Dinar (IQD), in a context of increasing global interest in investing in markets with sustained growth potential.
The Recovery of the Iraqi Dinar and Its Context
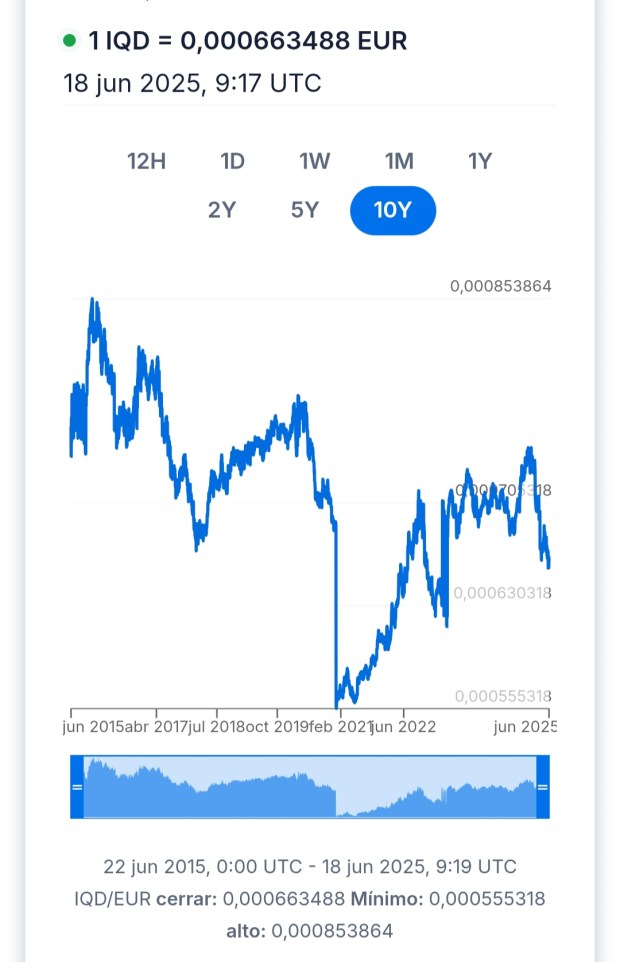
Since approximately EUR 0.000555 per IQD in 2015, the Dinar has experienced fluctuations, including a decline in 2021, but has shown a recovery trend, reaching around EUR 0.00066348. This increase reflects an economy in the process of stabilization and growth, with signs of greater international confidence—especially in a country endowed with vast oil reserves and ongoing reforms. The appreciation of the Dinar indicates resilience and a promising outlook for investors seeking diversification in emerging markets with significant resources.
Comparison with Other Emerging Markets in the Middle East
When analyzing Iraq alongside Ethiopia and Pakistan, it becomes evident that although these countries share the characteristic of being developing economies, they exhibit distinct profiles and challenges:
- Ethiopia: Experiencing rapid economic growth driven by agriculture and manufacturing, Ethiopia boasts robust growth rates; however, it faces challenges related to inflation and the devaluation of its currency, the Birr. Despite advances in infrastructure, political stability and inflation control are still ongoing processes.
- Pakistan: Focused on anti-inflation measures, reforms, and growth prospects, Pakistan presents promising outlooks. Yet, it faces challenges related to political stability and high external debt, which create some risks for investors.
In contrast, Iraq, with its strategic oil reserves and structural reforms, presents a combination of evolving stability and growth potential that can be more attractive to certain investors looking at opportunities in the Middle East. Its energy resources and economic opening provide competitive advantages compared to other markets where political and economic risks are still being assessed.
Positive Factors and Success Cases in Iraq
The trend toward greater economic stability in Iraq is supported by several initiatives:
- Rising stability: The gradual recovery of the Dinar indicates that Iraq is moving toward a more solid macroeconomic environment.
- Natural resources and energy sector: With some of the world’s largest oil reserves, Iraq guarantees steady income and opportunities in energy, infrastructure, and technology sectors.
- Reforms and openness: The government has implemented structural reforms aimed at attracting foreign investment, modernizing key sectors, and reducing dependence on oil.
- Internal stability: Despite being in an unstable region, Iraq has demonstrated a trend toward internal order—overcoming the 2003 wars and terrorism. The country has managed to establish the rule of law and a stable society, which has been a decisive factor in its economic recovery and expansion efforts into new markets.
- Growth prospects: The trajectory of the IQD recovery could lead to future appreciation, benefiting early investors.
One notable success story in the Iraqi market is the expansion of the Basra refinery in the south of the country, which attracted foreign investment, primarily from China’s energy sector. This project has increased oil production capacity, generated employment, and transferred technology, strengthening Iraq’s image as a reliable and growing energy investment destination.
Simultaneously, the country’s internal stability, economic situation, and currency valuation make Iraq very attractive for other sectors such as import/export beyond oil and its derivatives.
Tourism, a vital sector for any country but highly sensitive to insecurity, is currently booming regionally due to internal stability and abundant natural riches — the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, deserts, northern mountains for nature lovers, as well as ancient cities like Uruk or Ur (where Patriarch Abraham was born), Babylon, Nineveh, and Baghdad. Sacred sites such as Kerbala and Najaf for Shia Islam or Lalish for the Yezidis are also important for tourism focused on history and culture.
Conclusion
Despite fluctuations in the market, the resilience and recovery of the IQD demonstrate that Iraq is on the path to consolidating its economy and expanding its regional influence. When compared to other emerging markets in the Middle East and Africa such as Ethiopia and Pakistan, Iraq presents clear competitive advantages, primarily because of its resources, ongoing reforms, and its relative political stability.
For long-term investors, Iraq offers an attractive opportunity to participate in an expanding economy with the potential for benefits that could multiply in the coming years as the country continues to strengthen its institutions, infrastructure, and international relations.
